R.E.News future Technology-The Balancing Act and the Science behind BallBot Control
 16/12/24-FR-English-NL-footer
16/12/24-FR-English-NL-footer
L’équilibre et la science derrière le contrôle du BallBot
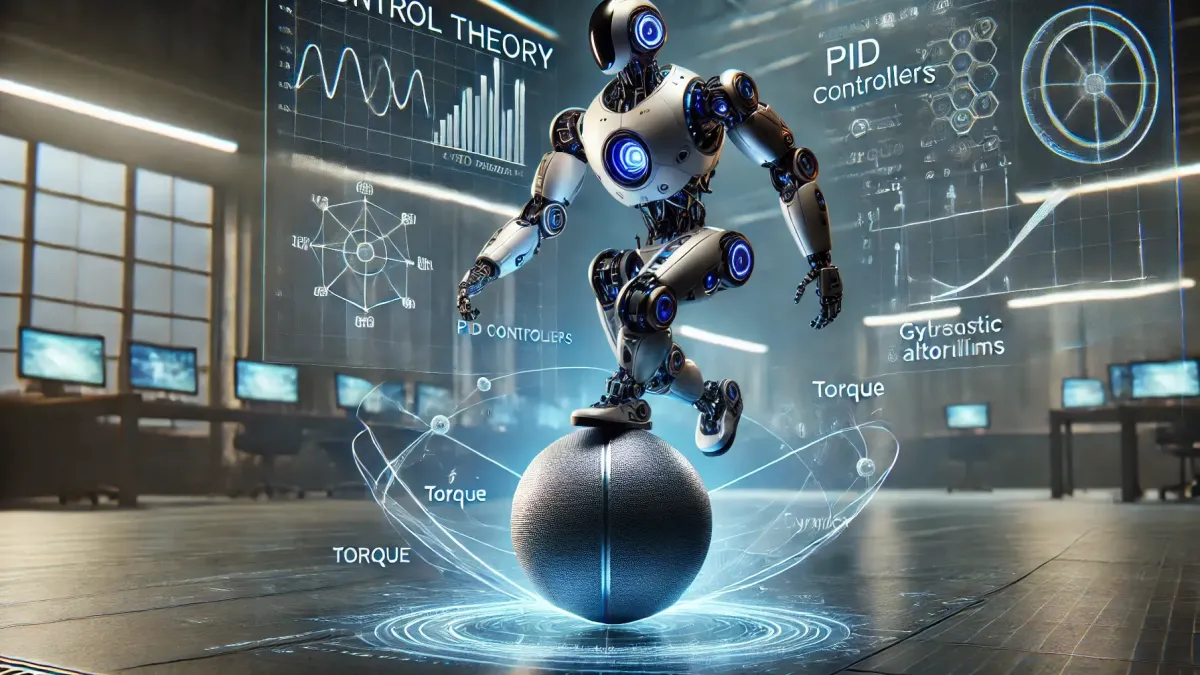

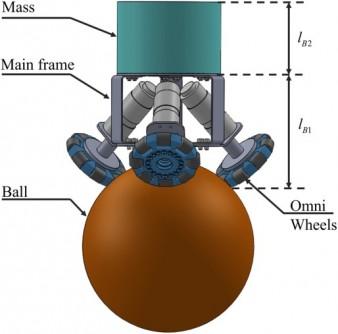 Image R.E.News- International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics Structure of the ball-balancing robot (BallBot). Image: International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics
Image R.E.News- International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics Structure of the ball-balancing robot (BallBot). Image: International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics
Dans le monde de la robotique en constante évolution, la quête d’autonomie et d’adaptabilité atteint de nouveaux sommets. Alors que les machines évoluent de plus en plus dans des environnements imprévisibles et dynamiques, le maintien de l’équilibre devient une capacité essentielle.
Parmi les nombreuses innovations dans le domaine, le BallBot, un robot en équilibre précaire sur une seule boule, se distingue comme une prouesse d’ingénierie remarquable. Les récentes avancées des chercheurs de la Faculté de génie mécanique de l’Université de Danang – Université des sciences et technologies, ont propulsé le BallBot vers un statut de partenaire indispensable dans les interactions homme-robot.
Leurs découvertes, publiées dans l’International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics, se penchent sur les complexités de la dynamique du BallBot, en introduisant des solutions de pointe pour améliorer sa stabilité et sa réactivité.
À première vue, la conception du BallBot semble presque magique : il se tient en équilibre sur une seule boule tout en conservant une maniabilité fluide. Sous son extérieur élégant se cache un système complexe d’ingénierie avancée. Les améliorations apportées par l’équipe de recherche comprennent un système de commande à quatre roues à boule inversée et un mécanisme de commande de lacet, qui confère au robot une capacité inégalée de rotation à 360 degrés sur son axe vertical.
Cette maniabilité améliorée permet au BallBot d’exceller dans les espaces restreints ou complexes où les robots à roues traditionnels hésitent. Mais ce n’est pas tout : lorsqu’il est stationnaire, un mécanisme de trépied rétractable assure la stabilité, évitant les chutes inutiles pendant les périodes de repos. La conception innovante n’est pas seulement une question d’esthétique ; c’est une leçon magistrale de fonctionnalité adaptée aux environnements humains dynamiques.
Le rôle de la planification de trajectoire dans une navigation fluide
L’une des avancées les plus marquantes du BallBot est l’intégration d’un algorithme de planification de trajectoire. Ce système permet au robot de passer gracieusement du repos au mouvement, en suivant des trajectoires prédéterminées avec précision.
En pratique, cela signifie que le BallBot peut se déplacer de manière fluide dans son environnement sans les mouvements saccadés typiques des robots moins sophistiqués. Qu’il s’agisse de naviguer dans un entrepôt encombré ou d’aider à une mission de recherche et de sauvetage à enjeux élevés, la capacité du BallBot à tracer et à exécuter des trajectoires fluides en fait un allié fiable.
Le Dr Nhu Thanh Vo, auteur principal de l’étude, explique : « Notre travail souligne l’importance d’affiner les configurations paramétriques pour optimiser les performances de contrôle du BallBot. En ajustant ces paramètres, nous pouvons améliorer la stabilité et la maniabilité du robot, ce qui est essentiel pour créer des robots plus efficaces et plus fiables qui peuvent aider dans une variété de situations. »
L’équilibre et la science derrière le contrôle du BallBot
Structure du robot à équilibrage de billes (BallBot). Image : International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics
Régulateur quadratique linéaire (LQR) en action
La pierre angulaire de cette recherche est la mise en œuvre d’un contrôleur de régulateur quadratique linéaire (LQR) – une approche mathématique sophistiquée pour optimiser les performances de contrôle. En s’appuyant sur le modèle LQR, les chercheurs ont affiné la dynamique de mouvement du robot, obtenant un équilibre optimal entre agilité et stabilité.
Ce mécanisme de contrôle avancé garantit que le BallBot reste stable même face à des perturbations externes ou à des changements brusques de direction. En substance, le modèle LQR donne au robot la capacité de « penser sur ses pieds », s’adaptant aux défis du monde réel avec une précision remarquable.
Les implications de cette recherche vont bien au-delà des limites du monde universitaire. Les robots d’équilibrage comme le BallBot ont un immense potentiel dans divers secteurs, notamment :
Fabrication et logistique : grâce à leur précision et à leur stabilité, les BallBots pourraient révolutionner les chaînes de montage, les opérations d’entrepôt et la manutention, rendant les processus plus rapides et plus sûrs.
Opérations de recherche et de sauvetage : dotés de la capacité de naviguer sur des terrains accidentés, ces robots pourraient devenir indispensables dans les zones sinistrées, atteignant des endroits inaccessibles aux humains.
Assistance médicale : bien que ce ne soit pas l’objet de cette étude, le potentiel des BallBots pour aider les personnes ayant des problèmes de mobilité mérite d’être souligné.
En abordant les défis de l’équilibre et du contrôle, cette étude pose des bases solides pour des robots capables de prospérer dans des environnements dynamiques, qu’il s’agisse de se déplacer dans une usine ou de fournir un soutien critique en cas d’urgence.
Si les progrès sont indéniablement impressionnants, les chercheurs reconnaissent que des défis subsistent. Le réglage fin des configurations paramétriques est une tâche complexe, qui nécessite une adaptation constante à de nouveaux environnements et à de nouvelles tâches. De plus, la mise à l’échelle de ces innovations pour la production de masse pourrait poser des obstacles.
Cependant, la trajectoire du progrès est claire. À chaque avancée, le rêve de robots entièrement autonomes et adaptables devient de plus en plus tangible. Le BallBot, avec sa conception et ses stratégies de contrôle de pointe, offre un aperçu de ce à quoi pourrait ressembler l’avenir de la robotique : fluide, stable et hautement interactif.
L’histoire du BallBot est celle d’une innovation et d’une exploration incessantes. En repoussant les limites de ce qui est possible en matière de robotique d’équilibrage, l’équipe de recherche de l’Université de Danang a tracé la voie vers des machines plus fiables, plus agiles et plus réactives.
Le BallBot n’est pas seulement une merveille technique ; c’est un symbole du potentiel des robots à devenir partie intégrante de la vie humaine, comblant le fossé entre l’intelligence artificielle et les fonctionnalités du monde réel. Alors que le domaine continue d’évoluer, une chose est claire : les robots d’équilibrage comme le BallBot sont sur le point de remodeler la façon dont nous envisageons la robotique et son rôle dans notre vie quotidienne.
NJC.© Info International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 16/12/24-English
16/12/24-English
The Balancing Act and the Science behind BallBot Control

 Image R.E.News- International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics Structure of the ball-balancing robot (BallBot). Image: International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics
Image R.E.News- International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics Structure of the ball-balancing robot (BallBot). Image: International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics
In the ever-evolving world of robotics, the quest for autonomy and adaptability is reaching new heights. As machines increasingly navigate unpredictable and dynamic environments, maintaining balance becomes an essential capability.
Among the many innovations in the field, the BallBot—a robot balanced precariously on a single ball—stands out as a remarkable feat of engineering. Recent advancements by researchers at the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, University of Danang – University of Science and Technology, have propelled the BallBot closer to becoming an indispensable partner in human-robot interactions.
Their findings, published in the International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics, delve into the complexities of the BallBot’s dynamics, introducing cutting-edge solutions to enhance its stability and responsiveness.
At first glance, the BallBot’s design seems almost magical—balancing atop a single ball while maintaining smooth manoeuvrability. Beneath the sleek exterior lies an intricate system of advanced engineering. The research team’s improvements include a four-wheel inverse mouse-ball drive system and a yaw drive mechanism, granting the robot an unparalleled ability to rotate 360 degrees on its vertical axis.
This enhanced manoeuvrability allows the BallBot to excel in tight or complex spaces where traditional wheeled robots falter. But there’s more—when stationary, a retractable tripod mechanism ensures stability, preventing unnecessary tumbles during rest periods. The innovative design isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s a masterclass in functionality tailored for dynamic human environments.
The Role of Trajectory Planning in Seamless Navigation
One of the most striking advancements in the BallBot is the integration of a trajectory planning algorithm. This system enables the robot to transition gracefully from rest to motion, following predetermined paths with precision.
In practice, this means the BallBot can move seamlessly across its environment without the jerky movements typical of less sophisticated robots. Whether navigating a cluttered warehouse or assisting in a high-stakes search-and-rescue mission, the BallBot’s ability to plot and execute smooth trajectories makes it a reliable ally.
Dr. Nhu Thanh Vo, the lead author of the study, explains: “Our work highlights the importance of fine-tuning parametric configurations to optimise the BallBot’s control performance. By adjusting these parameters, we can enhance the robot’s stability and manoeuvrability, which is key for creating more efficient and reliable robots that can assist in a variety of settings.”
The Balancing Act and the Science behind BallBot Control
Structure of the ball-balancing robot (BallBot). Image: International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics
Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR) in Action
The cornerstone of this research is the implementation of a Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR) controller—a sophisticated mathematical approach to optimising control performance. By leveraging the LQR model, the researchers fine-tuned the robot’s movement dynamics, achieving an optimal balance between agility and stability.
This advanced control mechanism ensures the BallBot remains steady even when faced with external disturbances or abrupt changes in direction. In essence, the LQR model gives the robot the ability to “think on its feet,” adapting to real-world challenges with remarkable precision.
The implications of this research extend far beyond the confines of academia. Balancing robots like the BallBot hold immense potential across various industries, including:
Manufacturing and Logistics: With their precision and stability, BallBots could revolutionise assembly lines, warehouse operations, and material handling, making processes faster and safer.
Search-and-Rescue Operations: Equipped with the ability to navigate uneven terrains, these robots could become indispensable in disaster-stricken areas, reaching locations inaccessible to humans.
Healthcare Assistance: Although not a focus of this study, the potential for BallBots to assist individuals with mobility challenges is worth noting.
By addressing the challenges of balance and control, this study lays a solid foundation for robots that can thrive in dynamic environments—whether it’s navigating a factory floor or providing critical support in emergencies.
While the advancements are undeniably impressive, the researchers acknowledge that challenges remain. Fine-tuning parametric configurations is a complex task, requiring constant adaptation to new environments and tasks. Additionally, scaling these innovations for mass production could pose hurdles.
However, the trajectory of progress is clear. With each breakthrough, the dream of fully autonomous, adaptable robots becomes increasingly tangible. The BallBot, with its state-of-the-art design and control strategies, offers a glimpse into what the future of robotics could look like—seamless, stable, and highly interactive.
The BallBot’s story is one of relentless innovation and exploration. By pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in balancing robotics, the research team at the University of Danang has charted a course for more reliable, agile, and responsive machines.
The BallBot isn’t just a technical marvel; it’s a symbol of the potential for robots to become integral to human life, bridging the gap between artificial intelligence and real-world functionality. As the field continues to evolve, one thing is clear: balancing robots like the BallBot are poised to reshape the way we think about robotics and its role in our everyday lives.
NJC.© Info International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 16/12/24-NL
16/12/24-NL
De Balancing Act en de wetenschap achter BallBot Control

 Image R.E.News- International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics Structure of the ball-balancing robot (BallBot). Image: International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics
Image R.E.News- International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics Structure of the ball-balancing robot (BallBot). Image: International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics
In de voortdurend veranderende wereld van robotica bereikt de zoektocht naar autonomie en aanpassingsvermogen nieuwe hoogten. Nu machines steeds vaker door onvoorspelbare en dynamische omgevingen navigeren, wordt het behouden van evenwicht een essentieel vermogen.
Van de vele innovaties op dit gebied springt de BallBot eruit als een opmerkelijke technische prestatie, een robot die wankel balanceert op één enkele bal. Recente ontwikkelingen door onderzoekers van de faculteit Werktuigbouwkunde van de Universiteit van Danang – Universiteit voor Wetenschap en Technologie, hebben de BallBot dichter bij een onmisbare partner in mens-robotinteracties gebracht.
Hun bevindingen, gepubliceerd in het International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics, duiken in de complexiteit van de dynamiek van de BallBot en introduceren geavanceerde oplossingen om de stabiliteit en responsiviteit te verbeteren.
Op het eerste gezicht lijkt het ontwerp van de BallBot bijna magisch: balancerend op één enkele bal terwijl het soepel blijft manoeuvreren. Onder het gestroomlijnde exterieur schuilt een ingewikkeld systeem van geavanceerde techniek. De verbeteringen van het onderzoeksteam omvatten een vierwielig omgekeerd muis-bal aandrijfsysteem en een yaw aandrijfmechanisme, waardoor de robot een ongeëvenaard vermogen heeft om 360 graden om zijn verticale as te draaien.
Deze verbeterde wendbaarheid zorgt ervoor dat de BallBot uitblinkt in krappe of complexe ruimtes waar traditionele robots met wielen falen. Maar er is meer: wanneer hij stilstaat, zorgt een intrekbaar statiefmechanisme voor stabiliteit, waardoor onnodige valpartijen tijdens rustperiodes worden voorkomen. Het innovatieve ontwerp draait niet alleen om esthetiek; het is een masterclass in functionaliteit die is afgestemd op dynamische menselijke omgevingen.
De rol van trajectplanning bij naadloze navigatie
Een van de meest opvallende ontwikkelingen in de BallBot is de integratie van een trajectplanningsalgoritme. Dit systeem stelt de robot in staat om sierlijk van rust naar beweging over te gaan, waarbij hij vooraf bepaalde paden nauwkeurig volgt.
In de praktijk betekent dit dat de BallBot naadloos door zijn omgeving kan bewegen zonder de schokkerige bewegingen die kenmerkend zijn voor minder geavanceerde robots. Of het nu gaat om het navigeren door een rommelig magazijn of het assisteren bij een belangrijke zoek- en reddingsmissie, het vermogen van de BallBot om soepele trajecten uit te stippelen en uit te voeren, maakt het een betrouwbare bondgenoot.
Dr. Nhu Thanh Vo, de hoofdauteur van de studie, legt uit: "Ons werk benadrukt het belang van het nauwkeurig afstemmen van parametrische configuraties om de besturingsprestaties van de BallBot te optimaliseren. Door deze parameters aan te passen, kunnen we de stabiliteit en wendbaarheid van de robot verbeteren, wat essentieel is voor het creëren van efficiëntere en betrouwbaardere robots die kunnen helpen in verschillende omgevingen."
De Balancing Act en de wetenschap achter BallBot Control
Structuur van de bal-balancerende robot (BallBot). Afbeelding: International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics
Lineaire kwadratische regelaar (LQR) in actie
De hoeksteen van dit onderzoek is de implementatie van een Lineaire kwadratische regelaar (LQR)-controller: een geavanceerde wiskundige benadering om de besturingsprestaties te optimaliseren. Door het LQR-model te benutten, hebben de onderzoekers de bewegingsdynamiek van de robot verfijnd en een optimale balans bereikt tussen wendbaarheid en stabiliteit.
Dit geavanceerde besturingsmechanisme zorgt ervoor dat de BallBot stabiel blijft, zelfs bij externe verstoringen of abrupte richtingsveranderingen. In essentie geeft het LQR-model de robot de mogelijkheid om 'op zijn voeten te denken' en zich met opmerkelijke precisie aan te passen aan uitdagingen in de echte wereld.
De implicaties van dit onderzoek reiken veel verder dan de grenzen van de academische wereld. Balancerende robots zoals de BallBot hebben een enorm potentieel in verschillende sectoren, waaronder:
Productie en logistiek: met hun precisie en stabiliteit kunnen BallBots assemblagelijnen, magazijnactiviteiten en materiaalbehandeling revolutioneren, waardoor processen sneller en veiliger worden.
Zoek- en reddingsoperaties: uitgerust met het vermogen om door oneffen terreinen te navigeren, kunnen deze robots onmisbaar worden in door rampen getroffen gebieden en locaties bereiken die voor mensen ontoegankelijk zijn.
Hulp bij gezondheidszorg: hoewel dit geen focus is van deze studie, is het potentieel van BallBots om mensen met mobiliteitsproblemen te helpen het vermelden waard.
Door de uitdagingen van evenwicht en controle aan te pakken, legt deze studie een solide basis voor robots die kunnen gedijen in dynamische omgevingen, of het nu gaat om het navigeren op een fabrieksvloer of het bieden van kritieke ondersteuning in noodsituaties.
Hoewel de vooruitgang onmiskenbaar indrukwekkend is, erkennen de onderzoekers dat er nog steeds uitdagingen zijn. Het nauwkeurig afstemmen van parametrische configuraties is een complexe taak, die constante aanpassing aan nieuwe omgevingen en taken vereist. Bovendien kan het opschalen van deze innovaties voor massaproductie obstakels opleveren.
De voortgang is echter duidelijk. Met elke doorbraak wordt de droom van volledig autonome, aanpasbare robots steeds tastbaarder. De BallBot, met zijn state-of-the-art ontwerp- en besturingsstrategieën, biedt een glimp van hoe de toekomst van robotica eruit zou kunnen zien: naadloos, stabiel en zeer interactief.
Het verhaal van de BallBot is er een van meedogenloze innovatie en verkenning. Door de grenzen van wat mogelijk is in balancerende robotica te verleggen, heeft het onderzoeksteam van de Universiteit van Danang een koers uitgezet voor betrouwbaardere, wendbaardere en responsievere machines.
De BallBot is niet alleen een technisch wonder; het is een symbool van het potentieel van robots om integraal onderdeel te worden van het menselijk leven, en de kloof te overbruggen tussen kunstmatige intelligentie en functionaliteit in de echte wereld. Terwijl het veld zich blijft ontwikkelen, is één ding duidelijk: balancerende robots zoals de BallBot staan op het punt de manier waarop we denken over robotica en de rol ervan in ons dagelijks leven te veranderen.
NJC.© Info International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Date de dernière mise à jour : 13/12/2024

















